In silico approaches supporting drug repurposing for Leishmaniasis
a scoping review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2024-7552Keywords:
neglected tropical diseases, computer-aided drug design, repositioning, docking, molecular dynamicsAbstract
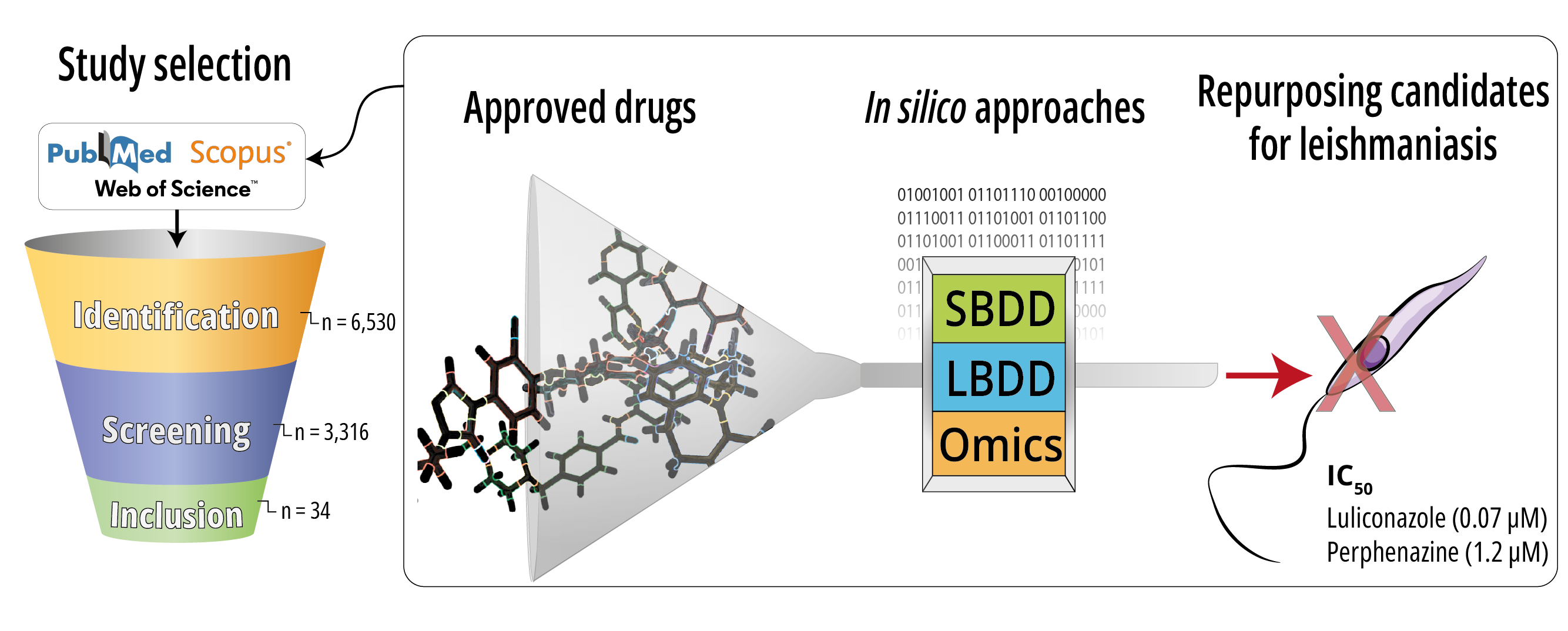
The shortage of treatment options for leishmaniasis, especially those easy to administer and viable for deployment in the world's poorest regions, highlights the importance of employing these strategies to cost-effectively investigate repurposing candidates. This scoping review aims to map the studies using in silico methodologies for drug repurposing against leishmaniasis. This study followed JBI recommendations for scoping reviews. Articles were searched on PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases using keywords related to leishmaniasis and in silico methods for drug discovery, without publication date restrictions. The selection was based on primary studies involving computational methods for antileishmanial drug repurposing. Information about methodologies, obtained data, and outcomes were extracted. After the full-text appraisal, 34 studies were included in this review. Molecular docking was the preferred method for evaluating repurposing candidates (n=25). Studies reported 154 unique ligands and 72 different targets, sterol 14-alpha demethylase and trypanothione reductase being the most frequently reported. In silico screening was able to correctly pinpoint some known active pharmaceutical classes and propose previously untested drugs. Fifteen drugs investigated in silico exhibited low micromolar inhibition (IC50 < 10 µM) of Leishmania spp. in vitro. In conclusion, several in silico repurposing candidates are yet to be investigated in vitro and in vivo. Future research could expand the number of targets screened and employ advanced methods to optimize drug selection, offering new starting points for treatment development.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Gustavo Scheiffer, Karime Zeraik Abdalla Domingues, Daniela Gorski, Alexandre de Fátima Cobre, Raul Edison Luna Lazo, Helena Hiemisch Lobo Borba, Luana Mota Ferreira, Roberto Pontarolo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





