Optimized therapeutic potential of Sijunzi-similar formulae for chronic atrophic gastritis via Bayesian network meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2024-7618Keywords:
chronic atrophic gastritis, Sijunzi-similar formulae, drug integration, Bayesian network meta-analysisAbstract
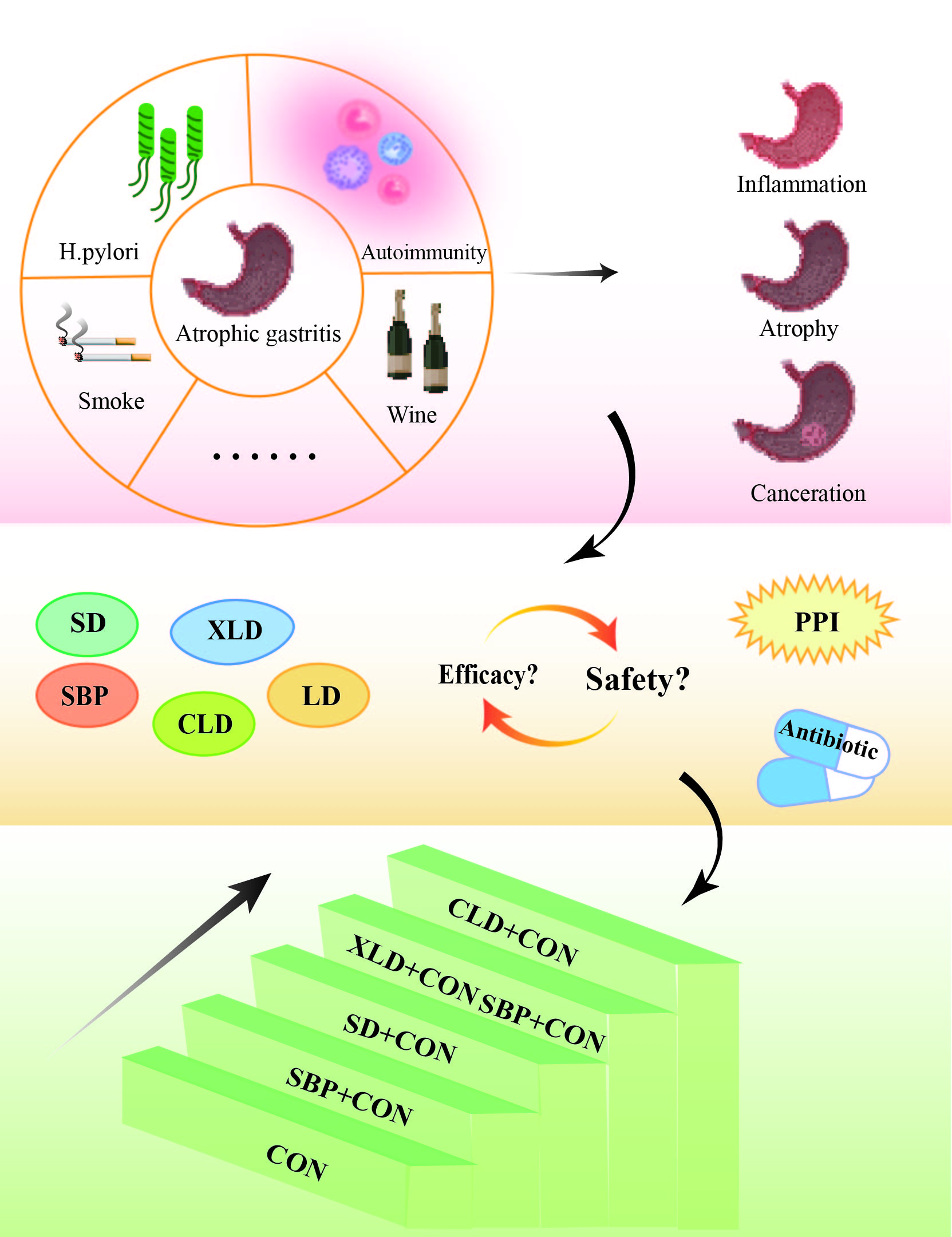
Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is considered as a significant risk factor for triggering gastric cancer incidence, if not effectively treated. Sijunzi decoction (SD) is a well-known classic formula for treating gastric disorders, and Sijunzi-similar formulae (SF) derived from SD have also been highly regarded by Chinese clinical practitioners for their effectiveness in treating chronic atrophic gastritis. Currently, there is a lack of meta-analysis for these formulae, leaving unclear which exhibits optimal efficacy. Therefore, we employed Bayesian network meta-analysis (BNMA) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SF as an intervention for CAG and to establish a scientific foundation for the clinical utilization of SF. The result of meta-analysis demonstrated that the combination of SF and basic therapy outperformed basic therapy alone in terms of clinical efficacy rate, eradication rate of H. pylori, and incidence of adverse events. As indicated by the SUCRA value, Chaishao Liujunzi decoction (CLD) demonstrated superior efficacy in enhancing clinical effectiveness and ameliorating H. pylori infection, and it also showed remarkable effectiveness in minimizing the occurrence of adverse events. Comprehensive analysis of therapeutic efficacy suggests that CLD is most likely the optimal choice among these six formulations, holding potential value for optimizing clinical treatment strategies.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Meilan Huang, Shiman Luo, Jiayue Yang, Huiling Xiong, Xiaohua Lu, Xiao Ma, Jinhao Zeng, Thomas Efferth

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





