Advances in cartilage tissue regeneration
a review of stem cell therapies, tissue engineering, biomaterials, and clinical trials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2024-7088Keywords:
cartilage regeneration, stem cells, tissue engineering, biomaterials, 3D bioprinting, clinical trials, organ-on-chipAbstract
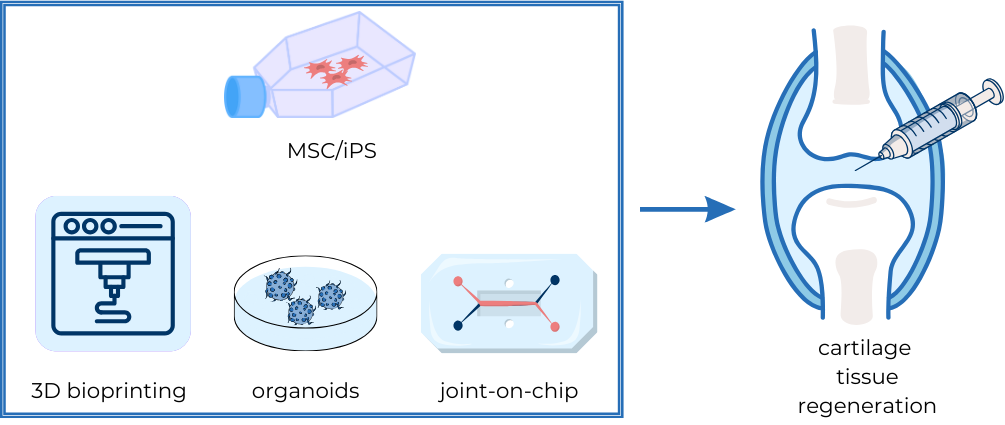
Cartilage tissue, characterized by its limited regenerative capacity, presents significant challenges in clinical therapy. Recent advancements in cartilage regeneration have focused on integrating stem cell therapies, tissue engineering strategies, and advanced modeling techniques to overcome existing limitations. Stem cells, particularly Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), hold promise for cartilage repair due to their ability to differentiate into chondrocytes, the key cells responsible for cartilage formation. Tissue engineering approaches, including 3D models, organ-on-a-chip systems, and organoids, offer innovative methods to mimic natural tissue microenvironments and evaluate potential treatments. MSC-based techniques, such as cell sheet tissue engineering, address challenges associated with traditional therapies, including cell availability and culture difficulties. Furthermore, advancements in 3D bioprinting enable the fabrication of complex tissue structures, while organ-on-a-chip systems provide microfluidic platforms for disease modeling and physiological mimicry. Organoids serve as simplified models of organs, capturing some complexity and enabling the monitoring of pathophysiological aspects of cartilage diseases. This comprehensive review underscores the transformative potential of integrating stem cell therapies, tissue engineering strategies, and advanced modeling techniques to improve cartilage regeneration and pave the way for more effective clinical treatments.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Julia Skoracka, Kaja Bajewska, Maciej Kulawik, Wiktoria M. Suchorska, Katarzyna Kulcenty

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





